Don't let slash chords confuse you too much. No, they are not the chords that the guitarist from Guns and Roses uses, they are something different. A slash is this: /, so a slash chord should have one of them in its name. These are all slash chords: G/B, C/Bb, F/G, Cmaj7/E. The symbol on the left of the slash is a chord and the symbol on the right is the bass note. So the slash chord G/B means that you have to play a G triad over a B bass note. If I wanted you to play this chord, I would probably say; "Play G on B" or "play G over B." There are basically two types of slash chords: one is an inversion of the chord itself, this makes the bass note (notated on the right of the slash) the 3rd, 5th or 7th of the chord. In the other type of slash chord, the bass note functions as the actual root of the chord. There is a gray area where these two types of slash chords overlap.
The first type of slash chords we will deal with are just simple triad inversions. Simply by voicing any triad with the 3rd or 5th in the bass will yield a slash chord. Ex: A simple C major triad voiced with the third, E as the bass note will yield a C/E slash chord, voiced with the 5th, G as the bass note will yield a C/G slash chord. When the triad has as the bass the root, it is said to be in root position. With the 3rd in the bass, 1st inversion and with the 5th in the bass, 2nd inversion.
| Bass Note | Inversion |
|---|---|
| 1 | root position |
| 3 | 1st inversion |
| 5 | 2nd inversion |
Play each inversion below. The roots are in black for reference:
The previous chord examples are just a few of the many triad voicings that can be constructed, see if you can come up with some more voicings of major triads. After you figure some more of the major voicings out, try to come up with the minor shapes also.
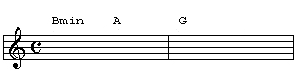
Why would you want to use the inversion anyways? These kinds of slash chords are often used to simply create chromatic bass movements in your chord progressions. Take a look at the chord progression below:
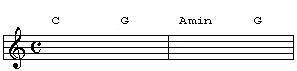
Although the bass movement works fine, we can create a smoother bassline by playing the G chord in 1st inversion. This will make the bassline for the first two chords descend chromatically:
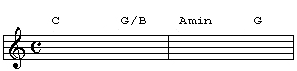
Let's take this concept a step further. Play the "before" version...

And now the "after" version. Check out how the bassline is completely chromatic for the first four chords:
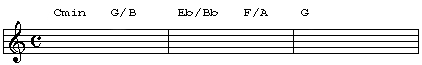
The first inversion major chord (3rd in the bass) is probably the most commonly used of the inversions. While triads in root position and in their inversions are the rule in pop and rock, you aren't likely to find triads in root position very often in Jazz, the 1st inversion major triad however can be found from time to time. Check out the example below:
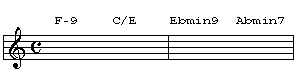
I used the previous chord progression in one of my own songs, "When Love Greets You.".
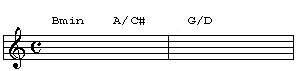
I'm going to show you how we can use slash chords to create contrary motion. In the chord progression below, the chords all descend in whole steps...
And once again the "after" version. While the chords descend in whole steps, the bassline ascends creating some musical interest.
Just as triads can be inverted, so can seventh chords. The 3rd, 5th and 7th can all be used as the bass note. As seventh chords are four note chords, we get the choice of four notes for our bass notes:
| Bass Note | Inversion |
|---|---|
| 1 | root position |
| 3 | 1st inversion |
| 5 | 2nd inversion |
| 7 | 3rd inversion |
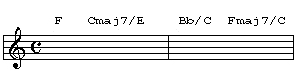
Some of the inversions work better than others. While the maj7th chord in first and second inversion sound beautiful, the 3rd inversion (7th in bass) sounds horrible. I couldn't even come up with a decent example for this lesson (give it a shot anyways, you never know). While the 3rd inversion for the maj7 chord sounds pathetic, the 3rd inversion of the dominant 7 chord (b7th in the bass) is somewhat common. Generally the inversions of the maj7 and dominant 7 chords are used more commonly than the inversions of the min7 chords, the min7 chord in first inversion simply turns into a maj6 chord. Ex: Amin7/C = C6. Try out the chord progression below and you'll hear how beautiful and spacious the maj7 chords in 1st and 2nd inversion sound. Oh yeah, I'll explain the Bb/C chord a little later, try not to think about it too much for now.
Creating complex harmony using slash chords - While the first kind of slash chords we worked with were simply inverted triads or 7th chords used to create a desired bass movement, the next type are something all together different. With triads and 7th chords, the bass note (on the right of the slash) is either the 3rd, 5th or 7th of the chord, in the next examples all the bass notes will be the actual roots. Before we start making some harmonically complex chords, let's first make some 7th chords by using the slash chord technique we studied in the previous examples. Examine the following Amin7 chord. If you look carefully you will find that the top three notes form a Cmaj triad. Therefore you can think of an Amin7 chord as a C triad simply placed over an A bass note, that's right: Amin7 = C/A.
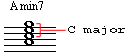
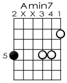
I moved the bass an octave lower than it is notated so we can hear the actual C triad over the A bass note.
As you discovered in the last example, 7th chords can be thought of as slash chords. I took the diatonic 7th chords of the C major scale and notated them as slash chords. Above the chord is the standard notated 7th chord name, below is the slash chord name:

I wrote the last example just to simply show you that you've been playing slash chords all along and might have never realized it. Before we move on to more complex harmony I need you to learn some simple triad shapes. The shapes are going to get put on top of various bass notes and open up into some pretty heavy chords. Generally major triads get used way more than minor triads for this kind of thing so I'm only going to cover them. Learn the following major triad shapes, roots are in black:
3rd string root major triads
4th (and 1st) string root major triads
2nd string root major triads
Before you go on to Part 2 of this article, make sure you have the previous triads down. Don't worry, this page will always be here waiting for you.
New Yorker Chris Juergensen is long time studio musician and session guitarist currently living and teaching in Japan.
His latest project is "Big Bad Sun", a CD traditional in nature, and contemporary in sound.